Indus River | Ganga River System | Brahmaputra River System: Hello All River system of India is much important to learning and understanding the geography of India. In this article we learn about approximately all the important river and their tributaries. This topic is very important regarding all the One-day, State PSC, UPSC and various competitive exam.

Drainage system (Drainage pattern)
Pattern of water flow into apparently format known as drainage and the network of this sort of flow is known as drainage system.
Drainage system is also known as River system in geomorphology segment of geography.
Drainage system is the result of nature geological time period slow and structure of rocks and soil.
River which drain into Bay of Bengal consisting of approximate77% of the total river weightage.
Example -Ganga, Godavari, Brahmaputra, Krishna, Cauvery etc.
River which drain into Arabian Sea consisting of approximate 25% of total river weightage
Example- Narmada, Sabarmati, Indus, Looni, Periyar.
Drainage system based on origin
1)Perennial rivers
2)Non-Perennial rivers
Perennial rivers consists of Himalayan river example Ganga, Indus, Brahamaputra and its all tributaries.
Non Perennial rivers consists of Peninsular river for example Godavari, Mahanadi, Krishna, Narmada, Cauveri river etc.
Drainage system based on Drainage pattern
Peninsular river ,Himalayan river and other coastal river that discharged into seawater.
River like Looni and Sambhar etc drains into inland part of India.
Contribution Percentage various River’s water
| River | Contribution % |
| Ganga | Approx 2.5% |
| Godavari | Approx 6.4% |
| Brahmaputra | Approx 40% |
| Mahanadi | Approx 3.5% |
| Narmada | Approx 2.9% |
| Krishna | Approx 3.4% |
And rest river contributes rest Percentage of water.
Differences Betweeen the river which drain into Bay of Bengal and which drain into Arabian Sea
| Arabian Sea drainage pattern | Bay of Bengal drainage pattern |
| 1)river discharge into Arabian Sea | 1) river discharge into Bay of Bengal |
| 2)its consists of 23% of drainage area | 2)its consists of 77% of drainage area |
| 3)it consist of west flowing river | 3)it consists of east flowing river |
Drainage pattern
1)Radial pattern- It consists of river originate from a hill or mountain and streamed/flow into all direction.
For example the River which originate from Amarkantak hills like Son and Narmada river.
2)Centripetal pattern– It consists of pattern in which water from all the direction drain into a lake
For example Manipur’s Loktak Lake.
3)Dendritic pattern- It consists of the pattern in which water flow look like tree branches with many twiges.
For example River of North India.
4)Trellis pattern- It consist of the pattern in which tributary of principal or main branches flow into parallel and tributaries make right angle with principal river.
For Example the river arises from Chota Nagpur’s Singhbhum region,Shivalik and laghu Himalaya.
Ganga River System
- Ganga is most crucial river regarding the cultural basin importance .
- Ganga originate from the Gangotri glacier near by Gomukh in UttarKashi district
- After originating its called as Bhagirathi.
- At DevPrayag Bhagirathi merges/meets with Alaknanda river ,after merging called as Ganga .
- After entering into the plain of Haridwar Ganga flows firstly south direction then southeast then east and lastly in the southern direction. Here it divided into two stream known as Hughli and Bhagirathi.
- Ganga river passes from the state of Uttrakhand,UP,Jharkhand,Bihar and west Bengal. Maximum length of Ganga is in UP.
Gangetic River system is the largest river system of India in all the river system.
Tributaries of Ganga –
Important major tributaries of Ganga are following
Right Tributaries-Son, Mahananda, Chambal, etc
Left Tributaries-Mahakali, Gandak, Karnali, Ghaghra, Damodar etc
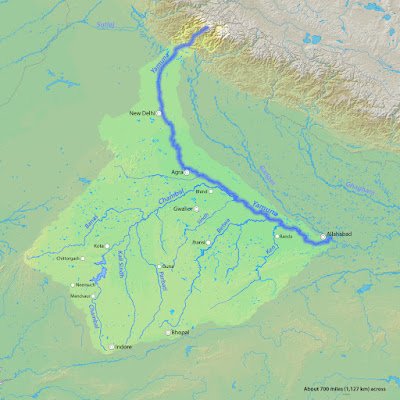
Yamuna River
- It originate from Yamunotri glaciers of Bunderpunchh range.
- Its largest tributary of Ganga
- It runs through state of UP, Uttrakhand,Haryana.
- It meets with Ganga at Triveni Sangam at Prayagraj(Allahabad).
- The largest tributaries of Yamuna is Tons river.
- Tributaries of Yamuna consists of Ken,Chambal,Betwa,Sindha,sarda,Giri,kunta,Hindon,RishiGanga,Kunta and Tons river.
Yamuna river Basin catchment area includes state of UP, Uttrakhand, Haryana, Rajsthan, Himanchal Pradesh, Delhi, Madhya Pradesh.
Chambal river originate from Plateau of Malwa near Mahu. It reaches Kota in Rajasthan in form of george in Northern direction. In Kota Gandhi Sagar Dam is built on this river. after that it merged with Yamuna river passing through to Bundi, Sawai Madhopur and Dholpur.
- Ghaghra river originate from Maapchachungo glacier. Sharda river merge with its in plane. after that this both merge with Ganga river in Chhapra district of Bihar.
- Damodar River originates from the eastern sites of Chhota Nagpur Plateau. It drains into Hooghly river passing through prolapse Valley. Barakar river is main tributary of Damodar River. Damodar Valley Corporation multi purpose Project built on it.
- The origination of Sharda river is Milam Glacier in Nepal it also famous as the name of Gauri Ganga. it is known as kali Ganga Too. it merge with Ghagra river near Barabanki district.
- Mahananda river originate from Darjeeling Hills.it is the the left Bank tributary of Ganga in west Bengal .
Peninsular River System
- it is much older than Himalayan rivers system
- Western Ghat act as water divider between the Peninsular river and the river which drain into Arab sea.
- the main source of the Peninsular river origination is Western Ghat.
- direction of the the Peninsular river is west to East direction. Narmada and Tapi are the exceptional.these flows in western direction.
- the main river of the peninsular River system is Mahanadi,Godavari,Krishna and Cauveri.these flow in the eastern direction. these rivers and other this sort of small rivers drain into Bay of Bengal.
- Peninsular river flows through the fixed Path, they did not make meanderandand they are not perennial river with maximum discharge of water in rainy day.
- Due to low gradient load carrying potential and velocity of river is much slow/low.
- These rivers create superimposed and rejuvenation drainage at few specific places. Yenna falls of Mahabaleshwar, Dhuandhar falls on the Narmada, Jog falls on the Sharvati etc are important waterfalls in Peninsular Region.
- Peninsular rivers make deltas at their mouths. But the west flowing rivers of Narmada and Tapi as well as those originating from the Western Ghats and falling in the Arabian Sea form estuaries.
Godavari River System
- Godavari River is the second-longest river in India. Its known as the name of Ganga of South.It consists of brownish water.
- Godavari originates from Trimbakeshwar(Nasik) in Maharashtra.
- due to the seasonal river it dried in the summers weather,widens and full during the monsoons season.
- Godavari river have many pilgrimage sites such as Bhadrachalam,Nashik and Traymbak.
- It has many important tributaries
- Right Bank Tributaries: Mula,Pravara, Manjra, Maner,Peddavagu etc.
- Left Bank Tributaries: Penganga,Dharna,Wardha,Wainganga, Pranahita, Kanhan, Indravati ,Sabari etc.
- Godavari river create a prolific delta at Rajahmundry.
- Important projects are situated at Godavari are SriSagar Dam, Godavari barrage, Upper Penganga, Jaikwadi, Upper Wainganga, Upper Indravati, Upper Wardha.
- there are many ongoing projects Prnahita-Chevala and Polavaram are few important of them.
- Godavari basin spread over the state of Karnataka,Odisha,Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh,few parts of Madhya Pradesh and Union territory of Puducherry.
Narmada River System
- Narmda rises from Amarkantak Hills in Madhya Pradesh.
- It flows through Maharashtra ,Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat and then drains into the Arabian Sea.
- Narmada flows west direction through a rift valley between the Vindhyan Range on the north and then Satpura Range in the south direction.
- It is the largest west flowing river of the South India.
- It creates Dhuan Dhar (Cloud of Mist) Falls near Jabalpur.
- Narmada river is bounded by the Maikala range on the East,Vindhyas on the North,the Arabian Sea on the west and Satpuras on the south.
- Narmada River basin spreads over the states of Gujarat, Maharashtra , Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh.
Mahanadi River
- Mahanadi originates from the northern foothills of Dandakaranya in Raipur District of Chhattisgarh state.
- Mahanadi has boundary with the the Eastern Ghats on the south, Central India hills on the northand east and on the west Maikale range.
- Mahanadi basin spread over states of Odisha ,Chhattisgarh and smaller parts of Madhya Pradesh,Jharkhand and Maharashtra.
- It has many tributaries
- Right bank Tributaries Tel ,Jonk and Ong.
- Left bank Tributaries Hasdeo,Mand and Seonath etc.
- India’s one of largest dam Hirakud Dam situated on this river.
- Mahanadi has the most-effectual sediment-depositing streams in the India.
- The famous pilgrimage site Puri is located at its mouth.
- Hirakud dam,Tandula reservoir in Chhattisgarh,Mahanadi delta project, Hasdeo Bango, Mahanadi Reservoir Project are situated in the Basin.
Krishna River
- Krishna River originates from the Western Ghats near in Maharashtra north of Mahabaleshwar.
- Krishna river flows through the states of Karnataka,Maharashtra,Andhra Pradesh, Telangana.
- Krishna river has following tributaries Left Bank tributaries Munneru,Musi and Bhima and Right bank tributaries Tungabhadra,Malprabha and Ghatprabha.
- Koyna is a small tributary of Krishna but known as Koyna Dam.
- Krishna river forms a large delta on the eastcoast.
- Krishna share its boundary with Western Ghats on the west ,Balaghat range on north, Eastern Ghats on the south .
- Important Hydro Power stations in the Krishna basin are Tungabhadara, Koyna, Bhadra,Sri Sailam, Nagarjuna Sagar,Naryanpur etc
Tapti River
- Tapti river originates near Multai reserve forest in Madhya Pradesh.
- Tapti river drains into the Arabian Sea by the Gulf of Cambay.
- Tapti river basin spread over states of Gujarat,Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra.
- there are following tributaries of Tapti river. Left Bank tributaries are Sipna,Mona ,Vaghur,Amravati,Buray, Panjhra, Bori, Girna, Purna And Right bank tributaries are Aner,Suki,Arunavati and Gomai.
- Dahigam Weir of Girna Project and Girna Dam,Hathnur Dam of Upper , Tapi Project (M.H.), Dam of Ukai Project and Kakrapar weir (Gujarat) are the important projects on this river.
Mahi River
- It originates from the north slopes of Vindhyas ranges in the Dhar district of Madhya Pradesh.
- Its creates boundary with Malwa Plateau on the east,Aravalli hills on the north and north-west,Gulf of Khambhat on the west and Vindhyas on the south direction.
- Mahi basin spreads over states of Gujarat,Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan.
- Kadana Dam and Mahi Bajaj Sagar dam are the hydro power station situated on this.
Sabarmati River
- Sabarmati originates from Aravalli hills in states of Rajasthan.
- Sabarmati river basin makes boundary with Rann of Kutch on the west,Gulf of Khambhat on the south and Aravalli hills on the north and northeast.
- Right bank tributary is Sei and Left bank tributaries are Hathmati,Vatrak,Wakal.
- Sabarmati reservoir project and Meshwo reservoir project are main project situated at this.
Luni River
- Luni originates from the Aravalli ranges near Ajmer. it drains into the Rann of Kachchh.
- Its make arid zone in western Rajsthan.
- Its known as Salt River too.
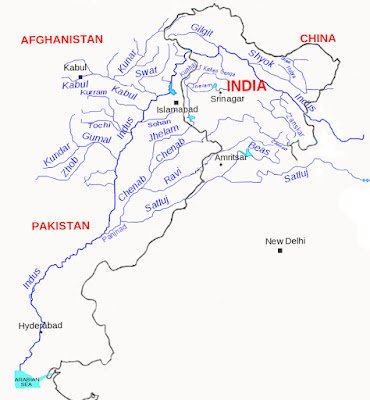
Indus River System
- Its one of the world’s largest basin.
- its originates near Bokhar Chu in Kailash mountain range.In Tibet its called as SingiKhamban or SherMukh .
- Many tributaries of Indus originates from the Himalaya like as Shyok, Nubra, Dras, Hunja, Shigar, Gilgit and Gausting.
- Our country India got her name from Indus river.
- Indus river drains into Arabian Sea.
- Major tributaries of Indus river system are Jhelum, Rabi, Beas, Chenab and Sutlej.
Order of direction from West to East
Jhelum, Chenab, Rabi, Beas, Sutlej
Chenab River
- It originates from near the Bara Lacha Pass of the Zaskar Range in Himanchal Pradesh.
- Its largest tributaries of Indus river.
- Its formed after merging the water of two river Chandra and Bhaga.
- Both of two river meets with each other near Kelang in Himanchal Pradesh.
Chenab river enters into the plain in Jammu Kashmir at Akhnur.
Beas River
- Beas originates near Beas Kund of Rohtang Passes.
- Beas merges with Sutlej in Punjab at Harike.
- Its smaller river in length and lies entirely in India.
Satluj River
- Satluj originates from the Manasarovar (Tibet) near Rakshas Lakes. Its known as the name of Logchain Khambab.
- Satluj cuts a gorge in Naina Devi Dhar. Most prominent Bhakra dam is situated on it.
Jhelum River
- It originate from the VeriNag falls situated in the PeerPanjal glacier in southeast part of kashmir Valley.
- Jhelum merges with Chenab at Trimmu.
- Jhelum flows northwards into Wular Lake here it changes its course southwards direction.
Rabi River
- It originates from western of Rohtang Pass in Kullu hills.
- It flows through Chamba Valley.
- Its origination place is much close to origination of Beas river.
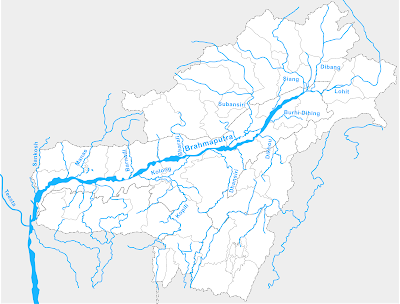
Brahmaputra River System
- Brahmaputra originate fro Chemayungdung glacier in southwestern Tibet.Its much close to the origination places of Indus and Satluj.
- It has many tributaries in Tibet.Important tributary is the Raga Tsangpo merging with Tsangpo near Lhatse Dzong.
- In Tibet Its known as Sangpo.
- In China Its known as Yarlung Zangbo Jiangin.
- It flow in parallel with Himalaya in Eastern direction.
- It enter into India passing through the Sunsiri-Arunanchal’s Giri hills.
- Its known as Dihang in state of Arunanchal pradesh.
- In state of Assam its known as Brahmaputra.
- after entering into Bangladesh Its called as Jamuna River.
- After merging with Ganga River in Bangladesh its known as Padma River.
- Right Bank tributaries – Sankosh, Manas, Subansiri, Kameng
- Left bank tributaries– Dibang,Lohit, Dhansiri
- Subansiri is the largest tributary of Brahmaputra.
Manas River
- It creates itself a transboundary river in the Himalayan region between India and southern Bhutan.
- Its valley consists of two important reserve forest one is Royal Manas National Park of Bhutan and other is Manas wildlife sanctuary of india.
Teesta River
- Teesta originates from Tso Lhamo lake in North Sikkim in Himalayan ranges.
- Rangeet River is the main tributary of the Teesta.It is the largest river in Sikkim. Rangeet river merges with Teesta at Tribeni.
- The river then flows towards Rangpo where it creates border with Sikkim and West Bengal.
- The river flows through Bangladesh and ultimately merges with Brahmaputra.
Subansiri River
- Subansiri River is known as Gold River too because for its gold dust.
- It flows through Arunachal Pradesh in Subansiri District .
Kameng River
- Kameng River originates in Himalayan ranges in the Tawang district
- It flow through Assam and Arunanchal Pradesh.
- It creates boundary with West Kameng Districts and East Kameng District .
- Kaziranga National Park and Pakhui Wildlife Sanctuary are situated near this River.
Dibang River
- It originates from Himalaya nearer tothe Tibet border
- It visible from the hills to enter the plain area in the Dibang Valley district of Arunachal Pradesh
The Mishmi hills are found along the upper plain of the Dibang River.
You May Also Like✨❤️👇